Projects
Multi-core Process Queue Simulator
This project simulates a multi-core process queue that receive a series of jobs and schedule them to run on multiple CPU cores as separate processes using one of the selected scheduling policy (FIFO, Round Robin, MLFQ). The process queue as two components, a server and a client.
The server maintains a queue of running jobs, waiting jobs and schedule them according to the scheduling policies.
The client allows the user to send jobs for the server to schedule and query the status of running and waiting jobs. It supports sending the following commands to the server:
- ADD command : sends the "command" to the server to schedule
- STATUS : gets the summary of running and waiting jobs, average turnaround time and response time
- RUNNING : gets the list of all running jobs
- WAITING : gets the list of all waiting jobs
- FLUSH : removes all jobs and terminates all active or suspended processes
$ ./pq -h
Usage: ./pq [options]
General Options:
-h Print this help message
-f PATH Path to IPC channel
Client Options:
add COMMAND Add COMMAND to queue
status Query status of queue
running Query running jobs
waiting Query waiting jobs
flush Remove all jobs from queue
Server Options:
-n NCPUS Number of CPUs
-p POLICY Scheduling policy (fifo, rdrn, mlfq)
-t MICROSECONDS Time between scheduling
 Click here for Multi-core Process Queue Simulator repository
Click here for Multi-core Process Queue Simulator repository Rorschach Directory Scanner
This is a program that monitors a directory and examines all files under the directory to determine if any files have been created, modified or deleted. If any of those events occur, an action on the file would be executed if the name of the file matches any of the patterns specified in a rule file.
The rule file is a simple text file with lines in the format of:
EVENT PATTERN ACTION
To run the program, compile the source code with "make" and run the executable with the following arguments:
$ ./rorschach -h
Usage: rorschach [options] ROOT
Options:
-h Print this help message
-f RULES Load rules from this file (default is rules)
-t SECONDS Time between scans (default is 5 seconds)
 Click here for Rorschach repository
Click here for Rorschach repository Texas Hold'em Simulation with AI
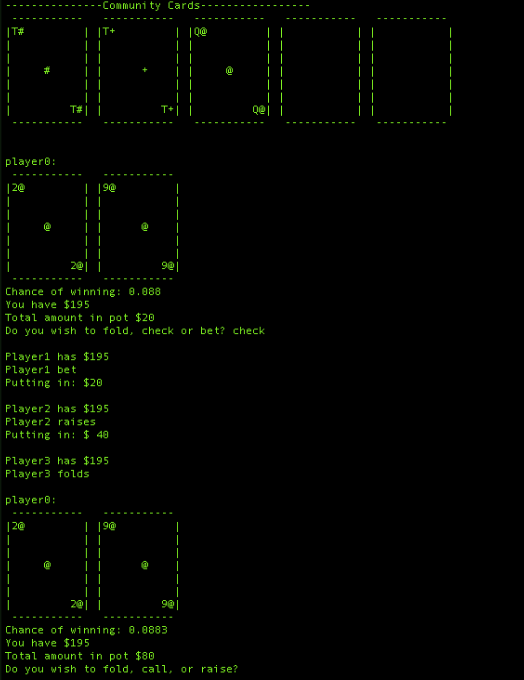
This is a fully implemented command-line based Texas Hold'em Poker Game with odd calculation. ASCII graphics and AI players using C++. It follows the fixed limited betting and ante rules. It utilizes the STL::<unordered_map> to store rankings of different hands and uses the Monte Carlo approach to simulate the probability of winning based on player's hand and the community cards.
 Click here for Texas Hold'em repository
Click here for Texas Hold'em repository Web Server
In my system programming course, one of the final projects was to create a web server which can handle file requests, CGI script requests and directory browsing requests. It was implemented using C system calls and can handle request one by one or by forking. A python script and several shell scripts were also created to benchmark the latencies and throughputs for forking and single. To see results of the benchmark and analysis, please click the link below to the blog post or read the README.md in the Github repository.
p.s. The thumbnail picture is a meme of one of my group members
 How forking affects latency and throughput of server
How forking affects latency and throughput of server  Click here for Web Server repository
Click here for Web Server repository Partial re-implementation of find
This is an partial re-implementation of the linux find command using C system calls that deal with files, directories, and processes. Similar to find, search recursively searches a directory and prints items it finds based on the specific options:
$ ./search -help
Usage: ./search PATH [OPTIONS] [EXPRESSION]
Options:
-executable File is executable or directory is searchable to user
-readable File readable to user
-writable File is writable to user
-type [f|d] File is of type f for regular file or d for
directory
-empty File or directory is empty
-name pattern Base of file name matches shell pattern
-path pattern Path of file matches shell pattern
-perm mode File's permission bits areexactly mode (octal)
-newer file File was modified morerecently than file
-uid n File's numeric user ID is n
-gid n File's numeric group ID is n
Expressions:
-print Display file path (default)
-exec cmd {} ; Execute command on path
 Click here for Search repository
Click here for Search repository